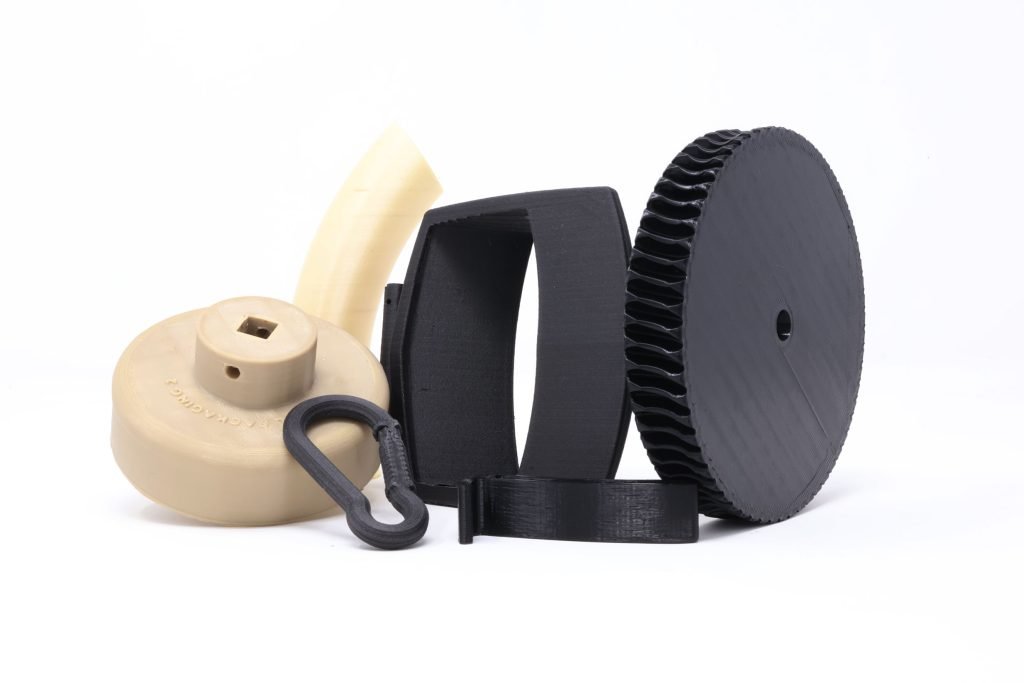
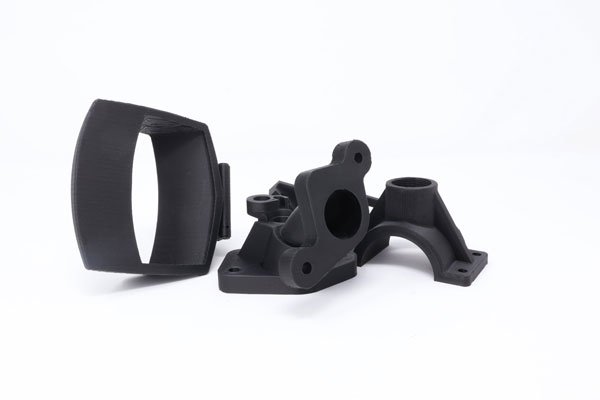
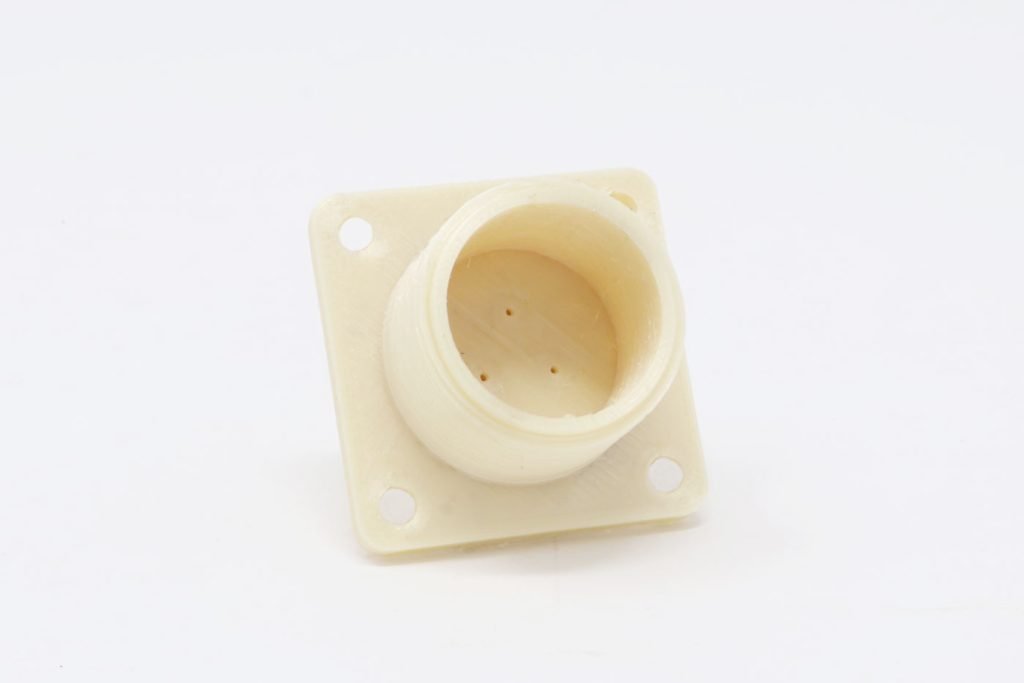
Fuse Deposition Modeling
Our FDM 3D printing service uses the latest cutting-edge printing techniques. Here at Surface Scan we can help bring your ideas or end use products to life. FDM is the most readily available printing technique and is generally considered a cheaper and faster alternative method of manufacturing, compared to other methods such as SLA or SLS. FDM utilizes a number of different printing material or filaments, all ranging in unique characteristics and proprieties making it perfect for an endless amount of applications.
FDM Materials
PLA
PLA produces more Eco-friendly parts. PLA is perfect for prototyping and non functional applications. has a faster lead time compared it’s alternatives, and is a favorite of those looking to quickly produce high quality 3D prints.
Strength 65%
Eco 90%
Durability 45%
Flex 30%
UV 30%
TPU
TPU offers a more flexible part. Its perfect for prototyping parts with flexible applications. TPU is typically used for those looking for 3d prints with more stretch or bend to them, it also comes in a rubber like finish making it perfect for the likes of phone cases.
Strength 70%
Eco 70%
Durability 75%
Flex 100%
UV 85%
PETG
PETG printed parts offer a more durable service. PETG is perfect for prototyping parts especially those with stronger applications. PETG has a higher tensile strength, impact resistance and flexibility compared to the likes of PLA
Strength 70%
Eco 90%
Durability 65%
Flex 50%
UV 70%
ASA
ASA 3D printed parts often have a similar tensile strength and durability compared to its alternatives. It does however have a higher UV & chemical resistance, making it the perfect choice of filament for those looking to print parts that will remain outside for extended periods of time.
Strength 75%
Eco 75%
Durability 65%
Flex 45%
UV 80%
Carbon Fibre
By infusing PETG filament with carbon fibre, you drastically increase its mechanical integrity. This lightweight material has a significantly higher tensile strength and stiffness. Parts are left with an attractive matte black finish.
Strength 77%
Eco 90%
Durability 75%
Flex 50%
UV 70%
PEEK
Our premium material for those needing industrial quality parts. Ultra-high strength and chemical resistance, PEEK maintains holds maintains its impressive properties even at severe temperatures.
Strength 100%
Eco 75%
Durability 100%
Flex 30%
UV 40%
Nylon PA6
Nylon PA6 strikes a great balance between performance and price, and is often used for functional prototypes or consumer goods. We also offer a variant reinforced with Carbon Fibre for added strength.
Strength 85%
Eco 90%
Durability 85%
Flex 35%
UV 50%
Ultem 9085
A chemically resistant thermoplastic, ideal for demanding applications, retaining durability even in harsh settings. Cheaper than PEEK if you can afford to sacrifice a little bit of strength and temperature resistance.
Strength 95%
Eco 75%
Durability 95%
Flex 45%
UV 75%
Start your FDM 3D print now...
Advantages Of FDM
Advantages to FDM
- Faster Lead Time
- Tough and Durable
- Cheaper than other printing processes
- Biodegradable
- Great prototyping applications
- Large variety of filaments


Colouring with FDM printers.
FDM allows your desired product to have almost any colour. As standard we print in black, grey, or white. We do however offer a number of other colours depending on what filament you choose, to name some we offer PLA and PETG in red, blue, green, orange and clear. On top of this it is possible to apply hand finises to your products, we recommend you do some further research.
All About FDM
Infill Rates
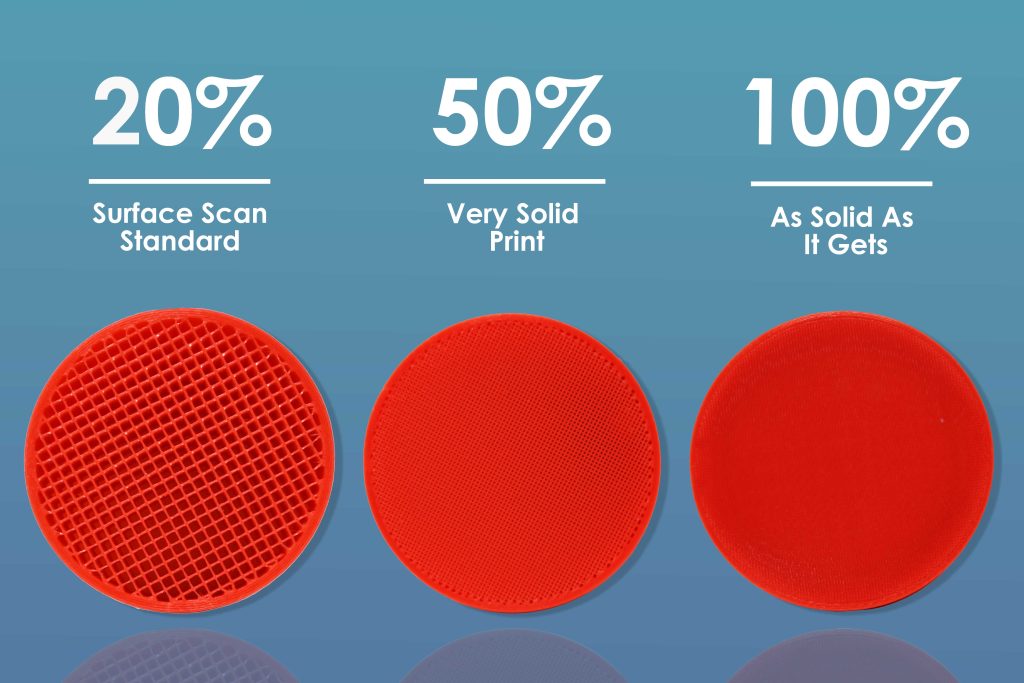
Above are three individual cross sections of three 3D printed cylinders, each of which demonstrates a different infill rate, 20%, 50%, and 100%. Our standard infill rate here at Surface Scan is 20% which not only allows your 3D printed parts to feel sturdy and secure but also remain lightweight and is the most cost-effective option. That being said for those looking to print parts that will undergo extended periods of stress or pressure we highly recommend you opt for a higher infill rate. Something to keep in mind is the higher the infill rate the longer the print time, and we would like to reassure you, no matter the infill rate you choose, your part will look exactly like the original file you supply us with, no changes or extra material will be seen on the exterior of your print, nor will it affect the outer shell or wall thickness, this is a separate measurement. This also includes size, the infill rate simply refers to the interior of your prints, the higher the rate the more honeycomb material is used (Pictured above).
Support Materials & Scaring
FDM or fuse deposition modeling is the process in which hot thermoplastic filament is fed through an extruder, heated, and laid across the printing bed layer by layer. Support material is vital in making sure this process proceeds without failing. More often than not your 3D-printed parts will contain what we call overhangs, overhangs occur when the nozzle extrudes the filament a fair distance past the previous layer, to the point it’s in mid-air. The filament, therefore, does not have the required support resulting in poor print quality. To combat this we use support material, to create scaffolding-type structures, giving the filament the support it needs. The support material does a fantastic job in assuring your parts print to a high quality and without fail, however, you can be left with support scaring, this is when the support material leaves slight marks or scaring on the print, especially on smaller more intricate prints, it is important to remember that support scaring does not always happen and can be fixed with some simple hand finishing.
Layer Lines
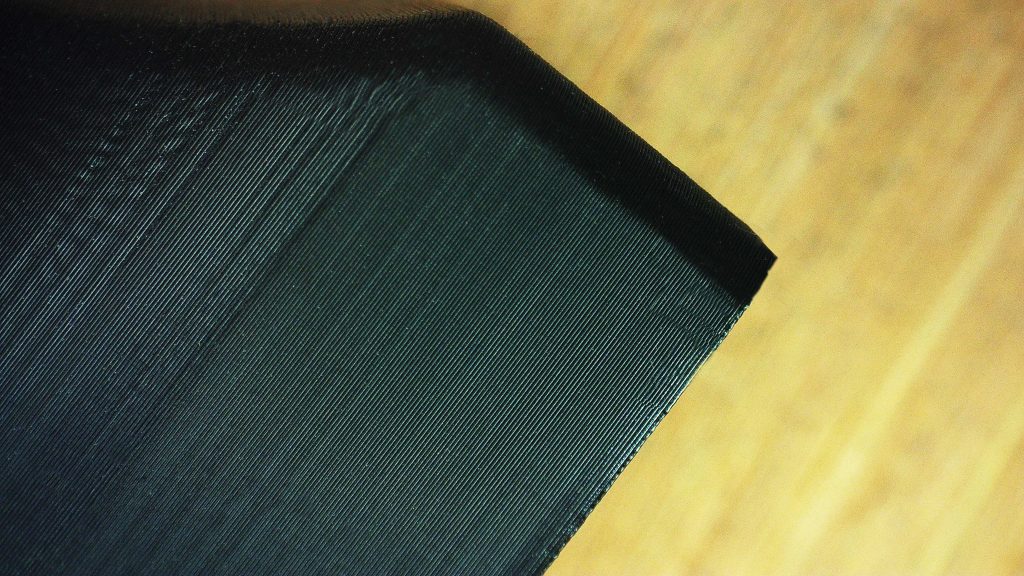

FDM follows the process of printing layer by layer. A by-product of this process is something called layer lines. These are lines in the print where each layer has been fused together. We here at Surface Scan print at a layer height of 0.2 mm, we find this to be a perfect middle ground for effective and efficient printing, whilst maintaining a high level of quality. This does mean the layer lines will be visible on your prints but not so that they distract you from the overall look and design of your 3D part. If you’re looking to remove all remnants of layer lines you can do so by applying wet and dry sanding, making sure not to heat the part as you do so, as this could damage the print itself. Instead, start off with low-grade sandpaper and work your way up until you are happy with the finish, we then recommend you apply a form of polish to get that final shiny aesthetic.
Brims & Helper Disks
Brims and helper disks are vital in making sure your 3D prints do not warp or become deformed, this happens when a 3D-printed object lacks sufficient adhesion to the printing bed, a way around this is to use brims or helper disk. So what are brims and helper disks, and how do they reduce deformed prints? A brim is a single layer of filament that surrounds the entire object whereas helper disks are small disks that are placed on the corners. Both helper disks and brims, eliminate corner lifting and warping by increasing the overall base surface area, ultimately increasing the overall adhesion of your prints to the printing bed. That being said it is important to remember that helper disks and brims are removed by hand, similar to support material, it is likely that some marks are left behind. This has nothing to do with the quality of the print but with the process of removal, these marks are small and can be tidied up by applying some basic hand finishes, including wet sanding and painting. Overall the brims and helper disk do a fantastic job at keeping your prints adhered to the printing bed with the slight drawback of some potential marks being left behind.
Wall Thickness
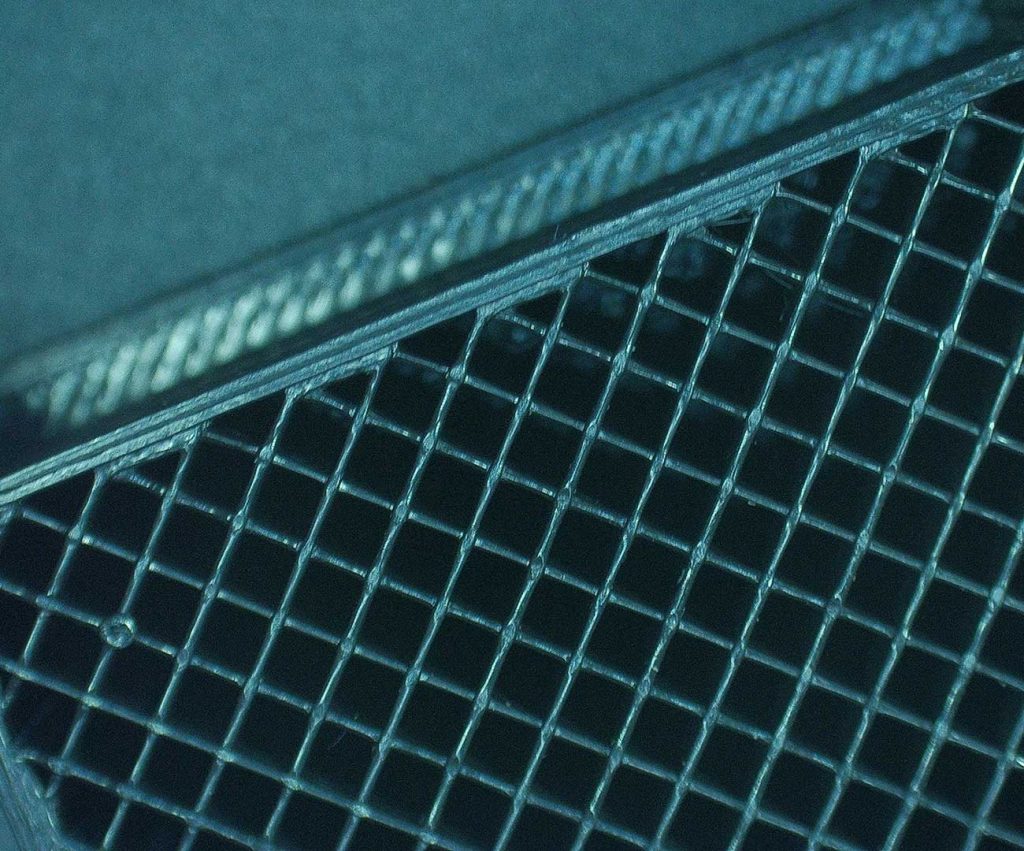
When talking about print wall thickness we are referring to the thickness of the shell or outer wall, here at Surface Scan we typically print at 2 walls thick, each wall coming in at 0.45mm creating a total of 0.90mm for the entire shell wall. This measurement is separate from the infill rate, each section is considered its own with its own measurements. The thickness of the wall will always remain at 0.90mm unless you have specifically asked otherwise. We find 0.90mm to be the perfect balance between durability, functionality, and overall aesthetic. It is important to keep in mind that no matter the infill rate the wall thickness will always remain the same, the higher the infill rate does not mean you’ll end up with a thinner wall to compensate, the wall thickness will stay 0.90mm at 20% infill and the same at 100% infill.
Things To Consider
FDM printing is fantastic at producing and reproducing parts effectively and efficiently, that’s not to say it doesn’t have limitations, here are the key limitations and some things to consider.
Fine Detail: I.E Warhammer
FDM works wonders for rapid prototyping making it perfect for those looking to get into 3D printing as a hobby, one type of print FDM typically struggles with is small parts with very fine detail, this mainly includes the likes of tabletop figures I.E Warhammer. Not to say they couldn’t be printed at all but a lot of the detail would be lost due to the sheer size of the print. Our printers use a 0.4mm nozzle so we are more than equipped for printing small or detailed prints but like everything, there is a limit. If you’re looking to print tabletop miniature we highly recommend either SLS or SLA, those types of prints are far better suited for injection modeling.
Surface finish: What to Expect
The second thing to consider is the overall surface finish of your print. FDM is wonderful at bringing your ideas and parts to life, and with a large range of materials, there is plenty of options when it comes to choosing functionality or appearance. PLA typically is the best of the bunch when opting for cleaner more shelf-ready prints, however, there are limitations to what can be printed. With FDM there are an endless amount of variables to consider, height, shape, supports, and time to name a few, these all factor into the overall quality and ultimately the finish of your print. FDM produces a near to perfect 3D representation of your original file, that being said it is important to take into consideration all of the above, you will not receive the same aesthetic as if you were to have gone down the injection molding route, again that’s not to say FDM can not produce the same quality it just requires some extra steps in the form of hand finishing.
Filament presence
This leads to the last two points of consideration, Visible seem and stringing. The seem refers to the point on the print where the filament starts and ends, which typically leaves an almost invisible line. most of the time it is impossible to find but on rare occasions, you will notice the points, However, like the layer lines, it should not take away from the overall look of your print. And lastly stringing, Stringing, also known as oozing occurs when the extruder moves to a new location, small strings of filament oozes out of the extruder as it moves on its path to the new location a common place to see stringing is on the ears of animal prints as the extruder moves in mid-air to the next ear. That being said we do try and combat stringing in a number of ways, these include using retraction settings, which help to pull back the filament when moving across open plains, Lowering the print temperature and speed, and lastly using dry filament. Of course, if any stringing still happens then it can be removed during the cleaning process.
FDM Batch Production
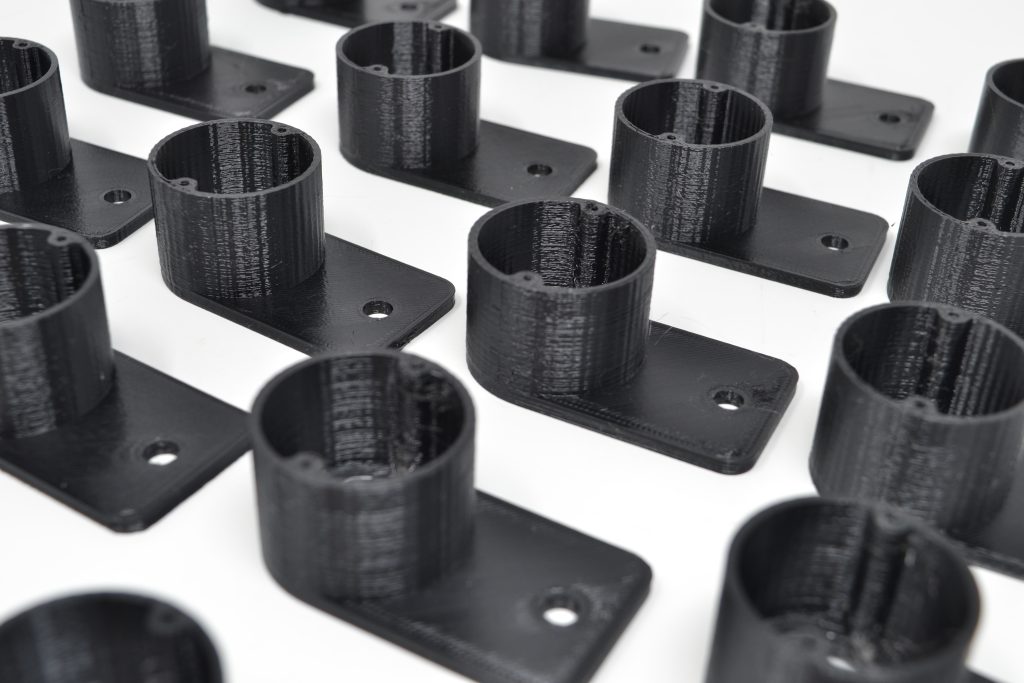

FDM excels when it comes to batch production, not only does it allow us to produce your parts in large volumes at rapid speeds but we can do so at extremely cost-effective rates. Unlike injection molding, FDM gives us much more accessibility when batch-producing your parts, not only do we have the freedom to prototype your part first for testing before committing to printing hundreds of parts, but we have more freedom with materials. FDM utilizes an array of different thermoplastics from PLA to ASA. With FDM batch production we are in no way restricted by molds, extremely high prices, or minimum order quantities. Therefore within limits, we can batch-produce any shape or orientation, bringing your parts to life on a large scale. Having the choice and capability to prototype your part first allows us to tweak and adjust your prints until they’re perfect, and without the restriction of molds, we can print any number of low to large-volume prints, from 100 to 5000 prints all done at an extremely cost-effective rate.

Rapid Prototyping
FDM and prototyping go hand in hand. Not only does FDM printing allow a person to delve deeper into designing, creating and producing the product of their dreams, it also allows those looking to get into a new hobby to do so, those who need a quick print to fix something around the house, or company to batch produce prototypes for testing then we here at Surface Scan highly recommend you try using FDM over the likes of SLS or SLA
Product Print Size
At Surface Scan we use a range of different FDM 3D printers, these have a bed size of 500mm X 500mm X 500mm. This allows us to print anything up to that size. However, if you or your company are looking to 3D print larger products, we here at surface Scan can split your 3D parts into smaller more manageable segments allowing them to fit on the 3D printers with great ease. Once all parts are printed they can be hand fished and fix or glued together

Filament Properties
Unlike SLS, FDM includes a number of largely differing filaments, all with a broad range of mechanical, industrial and functional applications. Just to list off a few, TPU has an excellent level of UV residence where as PLA simply does not, PETG has fantastic weather tolerance and ASA is great at printing 3D miniatures. FDM has a resolution of 50 to 200 microns, making it one of the more versatile ways of producing a large variety of components

What effect does FDM have on the environment?
Many people don’t know this but FDM printing is good for the environment, it reduces manufacturing waste and has a low carbon footprint. Most people only print what’s needed or what’s in demand. This means there is less waste when manufacturing. The filaments used are thermoplastic which can be reheated and reused. Printing farms and larger facilitates localize production meaning little energy is used when producing your custom parts. On top of this 3 out of the 4 FDM printing processes are biodegradable, ASA although not biodegradable can be recycled.
FAQ
How does FDM work?
FDM 3D printing is the process in which a thermoplastics filament of your choice, either PLA, TPU, PETG or ABS are extruded through either a direct or bowden extruder. The filament is heated to melting point and set layer by layer to the print bed. This is done over and over again until your 3D file is turned into a tangible 3D part. Depending on the overhangs and cavities of the print there will be support material that we here at Surface Scan remove for you.
Is FDM better than SLS?
FDM prints are of a lower quality when compared to SLS or SLA 3D prints, and therefore is not the best option when looking to print end-use, complex geometries in one. However, FDM makes up for it in print, speed, accessibility, hand-finish applications, and overall cheapness. FDM is by far better for the larger more simple prints that require a quicker print speed, There are definitely pros and cons for both, if you looking for larger, simple prints, prototyping, or a hobbyist we highly recommend FDM over SLS or SLA.
Is FDM food safe?
FDM is for the most part food safe, filaments like PETG and PLA are considered food safe whereas ABS is not, it is also to important to keep in mind that although the likes of PLA and PETG are considered to be safe they both fall short of full safety due to the nature of layer to layer adhesion, these layers in some place will have microscopic gaps, that are breeding ground for bacteria and often collect residue from the printer and any substance used in conjunction with the part, these gaps are extremely hard to clean properly.
Is FDM cheap?
The pricing for FDM will vary depending on the filament used, the size of the print and the size of the overall order, including how many prints or parts required. It is typically cheaper to print with FDM over the likes of SLS and SLA. PLA falls on the cheaper side of FDM and TPU on the more expensive.
How fast is FDM printing
The print speed again relies on the size of your print and the current demand of us here at Surface Scan. We offer three different types of shipping speed these are as follows,
Economy 7 to 10 - working days from your order date
Standard 3 to 7 - working days from your order date
Express 1 to 3 - working days from your order date
What does FDM stand for?
FDM in 3D printing stands for fused deposition modeling, might also be known as FFF or Fused filament fabrication.
Lets Talk
We’re ready for your enquiry. Please fill out the form, and someone will get back to you as soon as possible or give us a call, which ever suits you best.